The sufficiency of theory of planned behavior (TPB) is still being questioned although the model was validated in predicting a wide range of intentions and behaviors. Based on a comprehensive literature review, an extended TPB model of tourists was proposed to investigate relations among constructs of the model with the addition of motivation. The Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) of Icek Ajzen (1988, 1991) helps to understand how we can change the behavior of people. The TPB is a theory which predicts deliberate behavior, because behavior can be deliberative and planned. TPB is the successor of the similar Theory of Reasoned Action of Ajzen and Fishbein (1975, 1980). Aladdins Gold Casino Review.

Theory Of Planned Behaviour Gambling Strategies
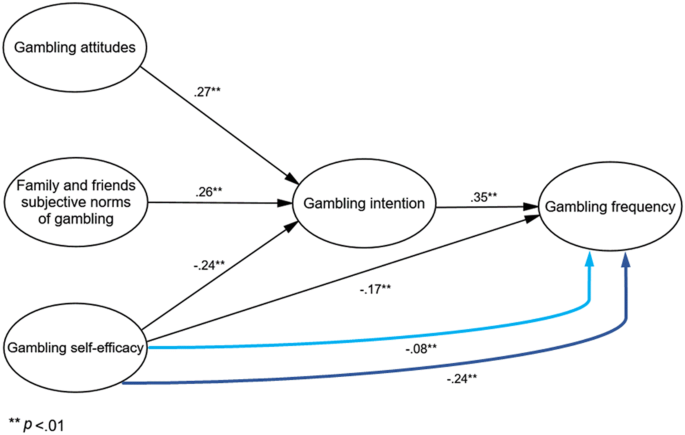
Theory of planned behavior (TPB; i.e., intentions, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, and attitudes) in past-year gambling and gambling frequency among college students. Results from this research support the utility of the TPB to explain gambling behavior in this population. Specifically, in TPB models to. The Theory of Planned Behavior upholds the key assumptions contained in the Theory of Reasoned Action, with certain modifications of its own. Deriving from the suppositions in TRA, the intentions of the individual largely reflects his personal attitudes, or their perception on the extent of favorability of an act. The theory of planned behaviour: reactions and reflectionsPsychology and Health, 26(9), 1113 - 1127. Ajzen, I., & Driver, B. Application of the theory of planned behaviour to leisure choice.
The theory of planned behaviour was developed by Icek Ajzen and describes the connection between one's beliefs and one's behaviours. This theory is an extension to Martin Fishbein's theory of reasoned action. Fishbein's theory asserts that if people believe that a behaviour is positive, and if they believe that it is a normal course of behaviour then they themselves will be more likely to adopt this particular behaviour and vice versa. So, according to Fishbein, an adoption of behaviours depends on people's belief on the attitude of the behaviour and their belief of the norm surrounding this behavior.

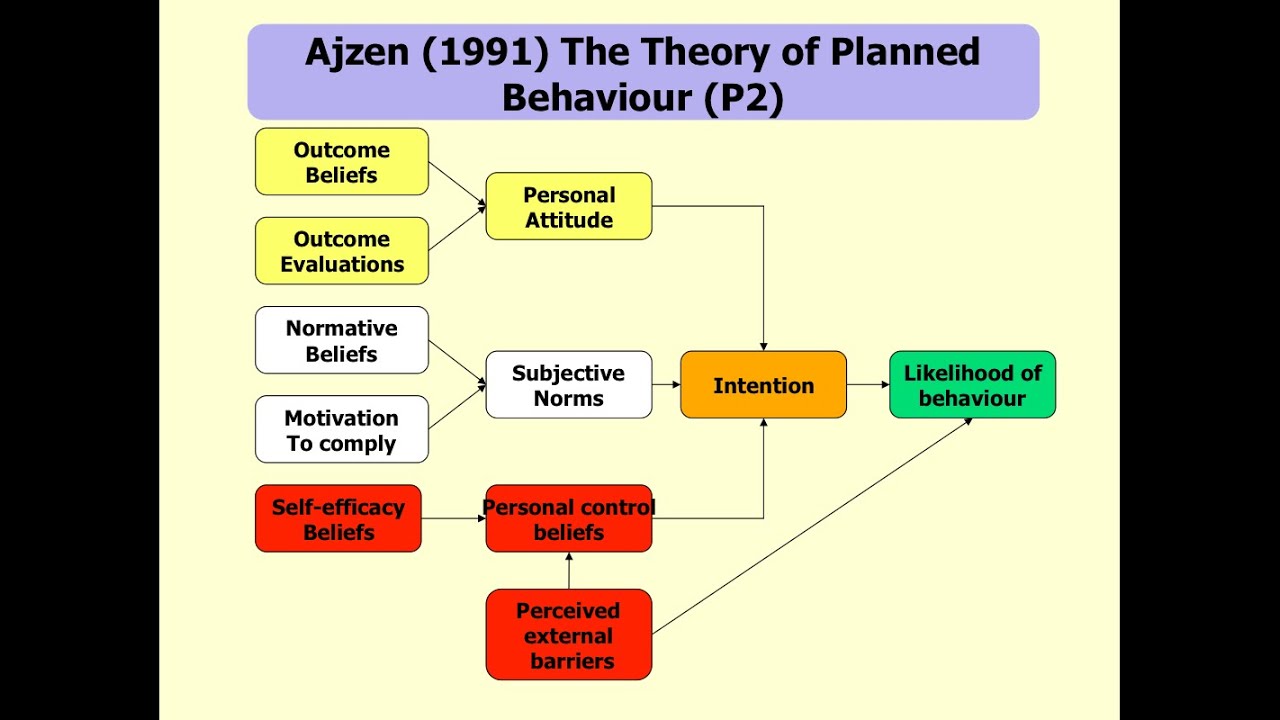
Ajzen builds on this by adding the notion of people's belief in their control over their own behavior. This is to account for the criticism that just because people plan to perform a certain behavior does not mean that they will actually act on it. For example, just because the night before you plan on getting up at 7am to go to the gym does not mean that when your alarm rings you actually will. According to the theory of planned behaviour, a higher perceived control over your own behaviour will give rise to a higher intention of performing a certain behaviour. Note that this does not actually translate into action.

Theory Of Planned Behaviour Gambling Strategies
Theory of planned behavior (TPB; i.e., intentions, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, and attitudes) in past-year gambling and gambling frequency among college students. Results from this research support the utility of the TPB to explain gambling behavior in this population. Specifically, in TPB models to. The Theory of Planned Behavior upholds the key assumptions contained in the Theory of Reasoned Action, with certain modifications of its own. Deriving from the suppositions in TRA, the intentions of the individual largely reflects his personal attitudes, or their perception on the extent of favorability of an act. The theory of planned behaviour: reactions and reflectionsPsychology and Health, 26(9), 1113 - 1127. Ajzen, I., & Driver, B. Application of the theory of planned behaviour to leisure choice.
The theory of planned behaviour was developed by Icek Ajzen and describes the connection between one's beliefs and one's behaviours. This theory is an extension to Martin Fishbein's theory of reasoned action. Fishbein's theory asserts that if people believe that a behaviour is positive, and if they believe that it is a normal course of behaviour then they themselves will be more likely to adopt this particular behaviour and vice versa. So, according to Fishbein, an adoption of behaviours depends on people's belief on the attitude of the behaviour and their belief of the norm surrounding this behavior.
Ajzen builds on this by adding the notion of people's belief in their control over their own behavior. This is to account for the criticism that just because people plan to perform a certain behavior does not mean that they will actually act on it. For example, just because the night before you plan on getting up at 7am to go to the gym does not mean that when your alarm rings you actually will. According to the theory of planned behaviour, a higher perceived control over your own behaviour will give rise to a higher intention of performing a certain behaviour. Note that this does not actually translate into action.
Theory Of Planned Behaviour Gambling Laws
The key concepts of the theory of planned behaviour are:
- Behavioural belief: an individual's belief about the consequences of certain behaviours.
- Attitude toward behaviour: positive or negative evaluation of self-performance of the behaviour.
- Normative belief: an individual's perception of social norms about the behaviour.
- Subjective norm: individual's perception of the particular behaviour influenced by the beliefs of significant others (family, friendsn etc,)
- Perceived behavioural control: individual's perceived ease or difficulty in performing a certain behaviour.
- Control beliefs: individual's beliefs about the factors that might help or impede performance of the behaviour.
- Behavioural intention: an individual's readiness to perform the particular behaviour.